Aptamer loaded MoS2 nanoplates as nanoprobes for detection of intracellular ATP and controllable photodynamic therapy†
Abstract
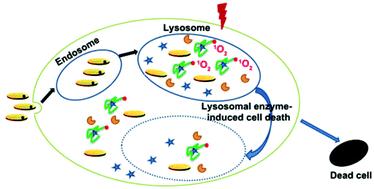
In this work we designed a MoS2 nanoplate-based nanoprobe for fluorescence imaging of intracellular ATP and photodynamic therapy (PDT) via ATP-mediated controllable release of 1O2. The nanoprobe was prepared by simply assembling a chlorine e6 (Ce6) labelled ATP aptamer on MoS2 nanoplates, which have favorable biocompatibility, unusual surface-area-to-mass ratio, strong affinity to single-stranded DNA, and can quench the fluorescence of Ce6. After the nanoprobe was internalized into the cells and entered ATP-abundant lysosomes, its recognition to ATP led to the release of the single-stranded aptamer from MoS2 nanoplates and thus recovered the fluorescence of Ce6 at an excitation wavelength of 633 nm, which produced a highly sensitive and selective method for imaging of intracellular ATP. Meanwhile, the ATP-mediated release led to the generation of 1O2 under 660 nm laser irradiation, which could induce tumor cell death with a lysosomal pathway. The controllable PDT provided a model approach for design of multifunctional theranostic nanoprobes. These results also promoted the development and application of MoS2 nanoplate-based platforms in biomedicine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...