Europium-engineered iron oxide nanocubes with high T1 and T2 contrast abilities for MRI in living subjects†
Abstract
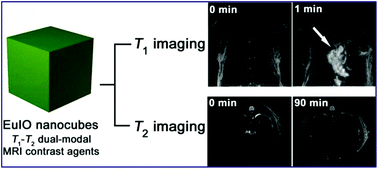
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents with both positive (T1) and negative (T2) contrast abilities are needed in clinical diagnosis for fault-free accurate detection of lesions. We report a facile synthesis of europium-engineered iron oxide (EuIO) nanocubes as T1 and T2 contrast agents for MRI in living subjects. The Eu(III) oxide-embedded iron oxide nanoparticles significantly increase the T1 relaxivity with an enhanced positive contrast effect. EuIO nanocubes with 14 nm in diameter showed a high r1 value of 36.8 mM−1 s−1 with respect to total metal ions (Fe + Eu), which is about 3 times higher than that of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with similar size. Moreover, both r1 and r2 values of EuIO nanocubes can be tuned by varying their sizes and Eu doping ratios. After citrate coating, EuIO nanocubes can provide enhanced T1 and T2 contrast effects in small animals, particularly in the cardiac and liver regions. This work may provide an insightful strategy to design MRI contrast agents with both positive and negative contrast abilities for biomedical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...