Molecular docking studies and 2D analyses of DPP-4 inhibitors as candidates in the treatment of diabetes†
Abstract
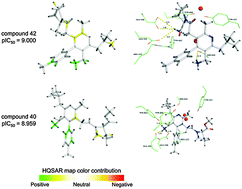
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) is an important biological target related to the treatment of diabetes as DPP-4 inhibitors can lead to an increase in the insulin levels and a prolonged activity of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP), being effective in glycemic control. Thus, this study analyses the main molecular interactions between DPP-4 and a series of bioactive ligands. The methodology used here employed molecular modeling methods, such as HQSAR (Hologram Quantitative Structure–Activity) analyses and molecular docking, with the aim of understanding the main structural features of the compound series that are essential for the biological activity. Analyses of the main interactions in the active site of DPP-4, in particular, the contribution of the hydroxyl coordination between Tyr547 and Ser630 by the water molecule, which is described in the literature as important for the coordinated interactions in the active site, were performed. Significant correlation coefficients of the best 2D model (r2 = 0.942 and q2 = 0.836) were obtained, indicating the predictive power of this model for untested compounds. Therefore, the final model constructed in this study, along with the information from the contribution maps, could be useful in the design of novel DPP-4 ligands with improved activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...