Integrating nanopore sensors within microfluidic channel arrays using controlled breakdown†
Abstract
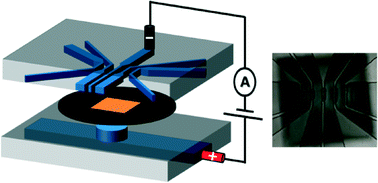
Nanopore arrays are fabricated by controlled dielectric breakdown (CBD) in solid-state membranes integrated within polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microfluidic devices. This technique enables the scalable production of independently addressable nanopores. By confining the electric field within the microfluidic architecture, nanopore fabrication is precisely localized and electrical noise is significantly reduced. Both DNA and protein molecules are detected to validate the performance of this sensing platform.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...