Mechanistic features of the copper-free Sonogashira reaction from ESI-MS†
Abstract
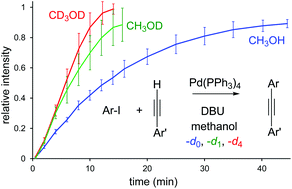
The mechanism of the Sonogashira reaction in methanol was studied in detail using pressurized sample infusion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (PSI-ESI-MS). Several key intermediates were identified and their structures were assigned by MS/MS studies. Cationic and anionic charged-tagged substrates were employed to look into the mechanism of this reaction from variety of angles. A reverse kinetic isotope effect was observed in which the reaction rate is accelerated in deuterated solvents (kH/kD = 0.6). The reaction was found to be zero order with respect to the aryl iodide and first order with respect to the phenylacetylene. A Hammett parameter of ρ = 1.4 indicates that the reaction is more favorable for aryl iodides with para EWGs. No evidence of product inhibition, dimerization of palladium catalyst, or agglomeration were observed. However, catalyst decomposition was inferred from a non-zero intercept in the plot of catalyst loading versus reaction rate. Monitoring the reaction by PSI-ESI-(−)MS on neutral and negatively charged substrates at variety of concentrations and conditions did not reveal any detectable anionic palladium complexes. Likewise no evidence of carbopalladation and relevant intermediates in the absence of a base was observed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...