Computer-assisted designed “selenoxy–chinolin”: a new catalytic mechanism of the GPx-like cycle and inhibition of metal-free and metal-associated Aβ aggregation†
Abstract
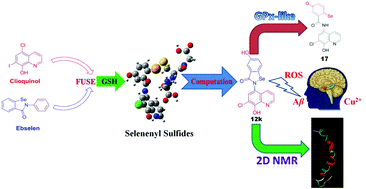
Using support from rational computer-assisted design, a novel series of hybrids (selenoxy–chinolin) designed by fusing the metal-chelating agent CQ and the antioxidant ebselen were synthesized and evaluated as multitarget-directed ligands. Most of the hybrids demonstrated significant ability to mimic GPx, which is highly consistent with the prediction results of DFT studies for the selenenyl sulfide intermediates in the computational design. Using 77Se, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy and high-resolution mass spectroscopy (HRMS), a novel catalytic mechanism, including a new selenium quinone active species, was first demonstrated. 2D NMR studies indicated that the typical hybrid has an effective interaction with Aβ. In addition, the optimal compound 12k was found to possess an excellent ability to scavenge peroxide and to inhibit self- and metal-induced Aβ aggregation, and an ability to disassemble preformed self- and metal-induced Aβ aggregates effectively. Furthermore, 12k was able to penetrate the central nervous system (CNS) and did not exhibit any acute toxicity in mice at doses up to 2000 mg kg−1. Overall, we demonstrated that hybrid 12k, through rational structure-based computational design, shows a potential for development as a therapeutic agent in AD.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...