Synthesis and anticancer activities of a novel class of mono- and di-metallic Pt(ii)(salicylaldiminato)(DMSO or Picolino)Cl complexes†
Abstract
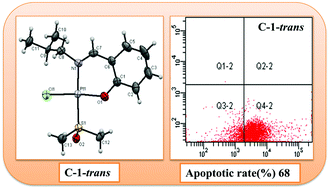
A series of novel Pt(II) complexes [cis- and trans-Pt(II)(salicylaldimine)(DMSO)Cl (C-1), trans-Pt(II)(salicylaldimine)(4-picoline)Cl (C-2), Pt(II)(salicylaldimine)Cl (C-3), trans- and cis/trans-Pt2(II)(salicylaldimine)(DMSO)2Cl2 (C-4), trans-Pt2(II)(salicylaldimine)(4-picoline)2Cl2 (C-5) was synthesized and characterized. The structures of C-1-cis, C-1-trans and C-3 were determined using a single crystal X-ray analysis. This class of Pt(II) complexes has been studied for their in vitro cytotoxicity in multiple human cancer cell lines, including breast (MCF-7), liver (HepG2), lung (A549), colon (HCT116) and cervical (Hela) cancers. C-1-trans, C-2 and C-4-trans showed significant cytotoxicity to these cancer cells comparable to cisplatin. A time- and dose-dependent MTT assay revealed that these complexes can suppress cell viability and cell proliferation. Mechanistically these complexes induced pro-apoptotic gene expression such as BAX, PUMA and NOXA and thereby enhanced apoptosis. Moreover, PARP cleavage in a dose-dependent manner indicated their cytotoxic effect against cancer cells. Apoptosis of cancer cells occurred through apoptotic pathways as explained by the cytometry analysis. The DNA unwinding properties of these active Pt(II) complexes were studied by gel electrophoresis using pBR322 plasmid DNA as a target. Changes in the morphology of cancer cells were also observed upon the addition of C-1-trans, C-2 and C-4-trans.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...