Fischer–Tropsch synthesis on Co/AlSBA-15: effects of hydrophilicity of supports on cobalt dispersion and product distributions†
Abstract
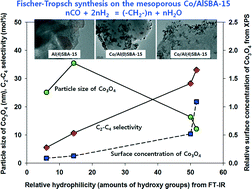
The surface properties of Al-incorporated ordered mesoporous SBA-15 (AlSBA-15) containing 25 wt% cobalt were studied for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS) reaction to verify the effects of hydrophilicity of the AlSBA-15 surfaces on the cobalt distribution and the product distribution, especially for C2–C4 hydrocarbons according to the contents of aluminum on the SBA-15. The AlSBA-15 was synthesized by varying the amount of Al2O3 in SBA-15 from 0.2 to 0.4 wt% during one-pot hydrothermal synthesis. The selectivity of C2–C4 hydrocarbons was increased with the increase in aluminum contents on the SBA-15 by showing higher olefin selectivity. The increased C2–C4 selectivity at similar CO conversions was mainly attributed to the formation of small cobalt particles with higher oxidation state, stronger metal–support interaction and less aggregation of particles on the outer surfaces of the AlSBA-15, which suppressed the secondary reactions of the olefins to heavy hydrocarbons in the regular mesopores of the acidic sites of the AlSBA-15. To understand the surface properties of Co/AlSBA-15 catalysts, the distribution and reduction behaviors of cobalt particles and the surface hydrophilicity (relative amounts of surface hydroxyl groups) of the Al-incorporated SBA-15 were characterized in terms of aluminum concentrations in the ordered mesoporous SBA-15.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...