Boron nitride coated rhodium black for stable production of syngas
Abstract
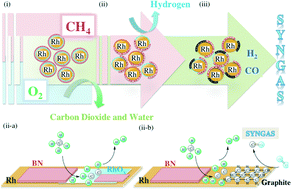
A blanket of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) was grown on rhodium black by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition. During methane oxidation at 650 °C the as-synthesized material showed steady syngas production shortly after oxygen interruption, whereas the activity of uncovered rhodium black degraded. The improved activity of the catalyst was attributed to the boron nitride coating, which serves to stabilize rhodium metal and avoid particle agglomeration by carbon deposition. These results present a compelling technique for metal catalyst modification with boron nitride in cases where coking is a problem.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...