Ab initio pressure-dependent reaction kinetics of methyl propanoate radicals†
Abstract
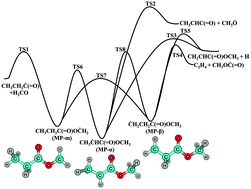
The unimolecular dissociation and isomerization kinetics of the three methyl propanoate (MP) radicals, CH3CH2C(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O)OĊH2 (MP-m), CH3ĊHC(
O)OĊH2 (MP-m), CH3ĊHC(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O)OCH3 (MP-α), and ĊH2CH2C(
O)OCH3 (MP-α), and ĊH2CH2C(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O)OCH3 (MP-β), are theoretically investigated using high-level ab initio methods and the Rice–Ramsperger–Kassel–Marcus (RRKM)/master equation (ME) theory. Stationary-point energies are obtained using the coupled cluster singles and doubles with perturbative triples correction (CCSD(T)), multi-reference singles and doubles configuration interaction (MRSDCI) with the Davidson-Silver (DS) correction, and multi-reference averaged coupled pair functional (MRACPF2) theories. The isomerization barriers between the three radicals are predicted to be generally lower than the corresponding bond dissociation channels, leading to a strongly coupled reaction system in subsequent kinetics studies. The phenomenological temperature- and pressure-dependent rate coefficients are computed using the RRKM/ME theory over a temperature range of 500 to 2000 K and at a pressure range of 0.01 atm to the high-pressure limit, which are then fitted to modified Arrhenius expressions. The β-scission rate coefficients of MP-α to CH3CHC(
O)OCH3 (MP-β), are theoretically investigated using high-level ab initio methods and the Rice–Ramsperger–Kassel–Marcus (RRKM)/master equation (ME) theory. Stationary-point energies are obtained using the coupled cluster singles and doubles with perturbative triples correction (CCSD(T)), multi-reference singles and doubles configuration interaction (MRSDCI) with the Davidson-Silver (DS) correction, and multi-reference averaged coupled pair functional (MRACPF2) theories. The isomerization barriers between the three radicals are predicted to be generally lower than the corresponding bond dissociation channels, leading to a strongly coupled reaction system in subsequent kinetics studies. The phenomenological temperature- and pressure-dependent rate coefficients are computed using the RRKM/ME theory over a temperature range of 500 to 2000 K and at a pressure range of 0.01 atm to the high-pressure limit, which are then fitted to modified Arrhenius expressions. The β-scission rate coefficients of MP-α to CH3CHC(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) and CH3Ȯ are predicted to be the smallest because of its highest activation energy among all studied unimolecular reactions channels. Analysis of branching fractions shows that both MP-m and MP-α radicals mainly decompose to the bimolecular products CH3CH2Ċ(
O) and CH3Ȯ are predicted to be the smallest because of its highest activation energy among all studied unimolecular reactions channels. Analysis of branching fractions shows that both MP-m and MP-α radicals mainly decompose to the bimolecular products CH3CH2Ċ(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) and H2CO, whereas the MP-β radical primarily decomposes via cleavage of a C–C bond to form C2H4 and CH3OĊ(
O) and H2CO, whereas the MP-β radical primarily decomposes via cleavage of a C–C bond to form C2H4 and CH3OĊ(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O). The isomerization channels dominate at low temperatures, the branching fractions of which decrease with increasing temperature and become very minor at about 2000 K. Our accurate rate coefficients and branching fractions help to illuminate the unique combustion properties of MP.
O). The isomerization channels dominate at low temperatures, the branching fractions of which decrease with increasing temperature and become very minor at about 2000 K. Our accurate rate coefficients and branching fractions help to illuminate the unique combustion properties of MP.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...