A durable surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate: ultrathin carbon layer encapsulated Ag nanoparticle arrays on indium-tin-oxide glass†
Abstract
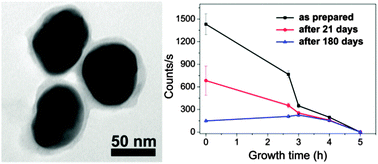
The application of Ag nanostructures to surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is hindered by their chemical instability. Fabrication of durable Ag-based SERS substrates is therefore of great significance in practical applications. In this work, ultrathin C-layer-encapsulated Ag nanoparticle arrays (UCL-Ag-NAs) are successfully fabricated on the surface of indium-tin-oxide (ITO) glass, using a hydrothermal method, for use as durable SERS substrates. The problem of Ag nanoparticles dissolving during the hydrothermal process is solved by using ZnO powder as a pH-buffering reagent. The SERS signal intensity of UCL-Ag-NAs decreases, accompanied by an improvement in Raman signal stability, as the C-layer thickness increases. Raman spectra show that the SERS signal intensities obtained from UCL-Ag-NAs with C-layers of 4.5 nm and 7.3 nm stored for 180 days are 64.9% and 77.8% of those obtained from as-prepared counterparts. The SERS intensity of the UCL-Ag-NA (C-layer of 4.5 nm) is 152.7% that of the bare Ag NA after 180 days of storage. XPS spectra confirm that the C-layer effectively suppresses the oxidation of the Ag NA. This methodology can be generalized to improve the durability of other dimensional Ag nanostructures for SERS applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...