Applicability of optimal functional tuning in density functional calculations of ionization potentials and electron affinities of adenine–thymine nucleobase pairs and clusters†
Abstract
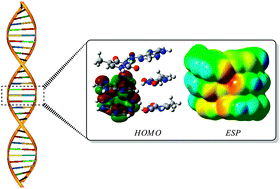
The intrinsic properties of DNA and RNA nucleic acid bases (NABs) such as ionization potentials (IPs) and electron affinities (EAs) are crucial to reveal various biochemical mechanisms. Successful application of density functional theory (DFT) using nonempirically tuned long-range corrected (LC) functionals for calculation of vertical ionization potentials (VIPs) and electron affinities (VEAs) of various adenine–thymine (AT) nucleobase pairs and clusters is demonstrated. We employ a tuning method by applying an asymptotically correct exchange–correlation potential adjusted to give frontier orbital energies (−εHOMO and −εLUMO) representing IPs and EAs and assess the quality of prediction which is comparable to high-level EOM-IP-CCSD/CCSD methods. The delocalization error calculated using different DFT functionals is quantified by calculations using fractional electron numbers. The cooperative effect of H-bonding and π-stacking on the IPs of AT clusters, as well as the reactivity parameters (global hardness and electrophilicity), is quantitatively characterized using the tuned LC functionals. The present work aims at providing a reliable and efficient theoretical tool for the prediction of the related electron donor and acceptor abilities of the NAB systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...