The effect of negative pressure aging on the aggregation of Cu2O nanoparticles and its application to laser induced copper electrode fabrication†
Abstract
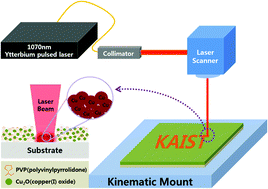
The aggregation and dispersion of nanoparticles are critical problems in selective laser sintering. In this study, negative pressure aging was applied to resolve the aggregation of nanoparticles and a metal oxide reduction method used to make a well-dispersed nanoparticles in solvent. As a result, metal oxide nanoparticles were synthesized according to a grade of the aggregation and aging conditions found to provide well-dispersed nanoparticles in solvent with less re-dissolution of the nanoparticles. Furthermore, a coating quality and characteristics of laser induced sintering were analyzed according to the grade of the aggregation. The coating quality was affected by the aggregation and the statistical dispersion of nanoparticles. The coating deposited by particles with a wide statistical dispersion has a better quality when compared with the coating prepared from particles with a narrow dispersion. The quality of laser sintered electrode depends on the aggregation but the dependency of the aggregation diminishes as the irradiation of the laser power is decreased.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...