Tuning the singlet–triplet energy gap of AIE luminogens: crystallization-induced room temperature phosphorescence and delay fluorescence, tunable temperature response, highly efficient non-doped organic light-emitting diodes†
Abstract
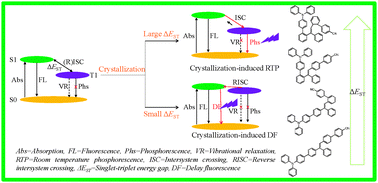
In this contribution, we finely tuned the singlet–triplet energy gap (ΔEST) of AIE-active materials to modulate their fluorescence, phosphorescence and delay fluorescence via rational molecular design and investigated the possible ways to harvest their triplet energy in OLEDs. Noteworthily, two molecules o-TPA-3TPE-o-PhCN and o-TPA-3TPE-p-PhCN with larger ΔEST values (0.59 eV and 0.45 eV, respectively) emitted efficient long-lived low temperature phosphorescence in their glassy solutions and exhibited efficient crystallization-induced room temperature phosphorescence (RTP). Meanwhile, it was the first time to observe a novel crystallization-induced delay fluorescence phenomenon in another AIE-active molecule p-TPA-3TPE-p-PhCN owing to its very small ΔEST value (0.21 eV). It was also found that molecules with various ΔEST values showed significantly different temperature sensitivity. Non-doped electroluminescent (EL) devices using these molecules as light-emitting layers were fabricated, exhibiting external quantum efficiencies (EQE) higher than theoretical values of purely singlet emitter type devices. Particularly, p-TPA-3TPE-p-PhCN showed outstanding device performances with high luminance and efficiencies up to 36 900 cd m−2, 11.2 lm W−1, 12.8 cd A−1 and 4.37%, respectively, considering that its solid-state quantum yield was only 42%. All the above observations suggested that tuning the ΔEST values of AIE materials is a powerful methodology to generate many more interesting and meaningful optoelectronic properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...