Highly effective photodynamic inactivation of E. coli using gold nanorods/SiO2 core–shell nanostructures with embedded verteporfin†
Abstract
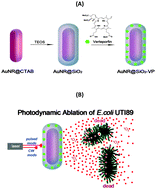
The potential of gold nanorods post-coated with a 20 nm silica shell loaded with verteporfin (Au NRs@SiO2–VP) as efficient near-infrared nanostructures for photodynamic therapy under continuous wave and pulsed-mode excitation to eradicate a virulent strain of E. coli associated with urinary tract infection is described.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...