DNA photocleavage in anaerobic conditions by a Ru(ii) complex: a new mechanism†
Abstract
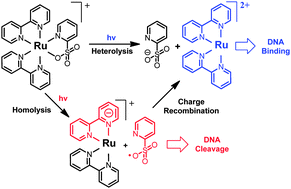
[Ru(bpy)2(py-SO3)]+ (bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine and py-SO3 = pyridine-2-sulfonate) was found to undergo py-SO3 dissociation upon visible light irradiation (≥470 nm) via Ru–O homolysis, producing reactive free radical species, and is thus able to not only photobind but also photocleave DNA in hypoxic conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...