Electrochemical detection of DNA by using “Pd/GO label copper stain” for signal amplification†
Abstract
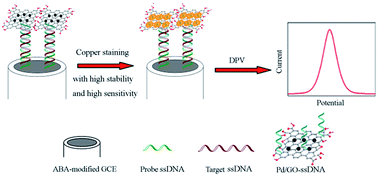
To overcome the problem of non-specific silver precipitation occurring in the traditional silver staining, this work presents a new strategy for signal amplification by labeling the biological molecule with Pd/GO nanoparticles (NPs), which further act as catalysts to reduce copper ions to metallic copper to enhance the signal (denoted as “Pd/GO label copper stain” later). Based on this strategy, the electrochemical detection of a single-base mutation associated with the breast cancer gene TOX3 is specially studied by employing differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). The analytical performance of this system shows that after 15 min of copper staining there is a linear relationship between the peak current resulting from the oxidative dissolution of the copper deposit and the logarithm of the target DNA concentration in the range of 10 μM to 1 pM. The limit of detection can reach 1 pM, which benefits from the high catalytic activity of Pd/GO NPs along with a low background level of “Pd/GO label copper stain”. Therefore, this process can be expected to be a good alternative to silver staining used in nanomaterial-based signal amplification strategies in future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...