Speciation and quantification of organotin compounds in sediment and drinking water by isotope dilution liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry
Abstract
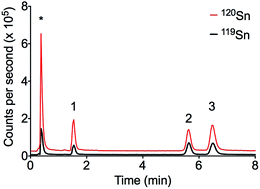
A rapid method was developed for the determination of monobutyltin, dibutyltin, tributyltin, monophenyltin, diphenyltin, and triphenyltin by liquid chromatography-isotope dilution-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry in sediments and drinking water. All six species were eluted in less than 6.5 minutes with a binary gradient. Offline solid phase extraction was used to pre-concentrate the organotin compounds for quantification employing two calibration procedures; external standard calibration and isotopic dilution. The external standard calibration approach yielded detection limits in the range of 1.5 to 25.6 ng L−1. The method was linear over four orders of magnitude with regression coefficients greater than 0.99 and a peak area repeatability less than 4.5% RSD (n = 7) for all compounds. The isotopic dilution method was three times more sensitive with detection limits in the range of 0.5–1.2 ng L−1. Recoveries for the external calibration method were from 33–68% with % RSDs of 5.7–12.7%. The isotopic dilution method had recoveries of 70–114% with % RSDs of 1.2–2.9%. The methods were applied to sediments sampled from the Cooks River in Sydney. The isotopic dilution method provided a viable alternative to the more common analysis by gas chromatography-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry for contaminated sediment without the requirement of sample derivatisation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...