A feasibility study of a pH sensitive nanomedicine using doxorubicin loaded poly(aspartic acid-graft-imidazole)-block-poly(ethylene glycol) micelles
Abstract
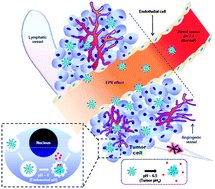
A polyelectrolyte block copolymer, poly(aspartic acid-graft-imidazole)-block-poly(ethylene glycol) (P(Asp-g-Im)-PEG), with several advantages such as an easy synthesis, having a high molecular weight and the buffer capacity of a zwitterionic polymer backbone compared to poly(histidine) backbones, was presently investigated to evaluate its feasibility as a pH sensitive anticancer nanomedicine. Doxorubicin (DOX) loaded P(Asp-g-Im)-PEG micelles (DPHAIM) were prepared by the bottom flask and diafiltration methods, forming stable pH sensitive nano-systems. DPHAIM with a 28% loading capacity displayed a pH dependent behavior with respect to drug release and cytotoxicity. At pH values below 7.0, the cumulative DOX release and cell cytotoxicity were increased compared to those at physiological pH. Animal imaging after intravenous administration of the micelles revealed their accumulation by passive targeting to tumor tissue compared to other normal tissues. This pH sensitive nanovehicle based on P(Asp-g-Im)-PEG is implicated as a promising anticancer nanomedicine with less toxicity on normal tissues for effective tumor treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...