Toward the enhanced photoactivity and photostability of ZnO nanospheres via intimate surface coating with reduced graphene oxide†
Abstract
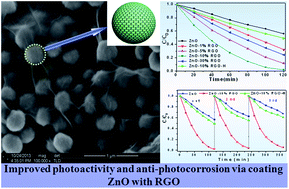
A series of uniform ZnO nanospheres–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites (ZnO–RGO NCs) with different weight addition ratios of RGO are successfully synthesized via a facile yet efficient method by intimately coating ZnO nanospheres (NSs) with RGO, which is afforded by electrostatic attraction between positively charged ZnO NSs and negatively charged graphene oxide (GO) in an aqueous medium at room temperature. The photocatalytic test of degradation of Rhodamine B shows that the optimal ZnO–10% RGO NCs exhibit a 5-fold enhancement of photoactivity than bare ZnO NSs, which is ascribed to the integrative synergetic effect of enhanced adsorption capacity, the decreased recombination of the electron–hole pairs and the enhanced ultraviolet light absorption intensity. Significantly, the recycled photoactivity tests show that, for ZnO–RGO NCs, the anti-photocorrosion of ZnO NSs is improved remarkably which is attributed to the effective hybridization of ZnO NSs with the RGO sheet via intimate surface coating. Such a significant photoactivity enhancement and anti-photocorrosion phenomenon can not be obtained by simply integrating RGO with ZnO NSs that are not subject to surface charge modification, which thus indicates the importance of intimate surface coating of ZnO with RGO toward the efficiency of enhancement of photoactivity and particularly the anti-photocorrosion of ZnO.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...