Dynamics of non-Brownian fiber suspensions under periodic shear
Abstract
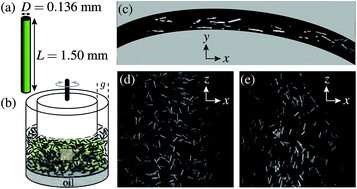
We report experiments studying the dynamics of dense non-Brownian fiber suspensions subjected to periodic oscillatory shear. We find that periodic shear initially causes fibers to collide and to undergo irreversible diffusion. As time progresses, the fibers tend to orient in the vorticity direction while the number of collisions decreases. Ultimately, the system goes to one of two steady states: an absorbing steady state, where collisions cease and the fibers undergo reversible trajectories; an active state, where fibers continue to collide causing them to diffuse and undergo irreversible trajectories. Collisions between fibers can be characterized by an effective volume fraction Φ with a critical volume fraction Φc that separates absorbing from active (diffusing) steady states. The effective volume fraction Φ depends on the mean fiber orientation and thus decreases in time as fibers progressively orient under periodic shear. In the limit that the temporal evolution of Φ is slow compared to the activity relaxation time τ, all the data for all strain amplitudes and all concentrations can be scaled onto a single master curve with a functional dependence well-described by t−β/νRe−tR, where tR is the rescaled time. As Φ → Φc, τ diverges. Therefore, for experiments in which Φ(t) starts above Φc but goes to a steady state below Φc, departures from scaling are observed for Φ very near Φc. The critical exponents are measured to be β = 0.84 ± 0.04 and ν = 1.1 ± 0.1, which is consistent with the Manna universality class for directed percolation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...