Facile preparation of monolithic κ-carrageenan aerogels†
Abstract
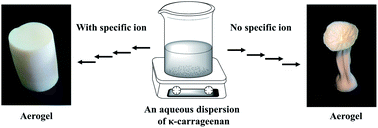
To the best of our knowledge, it is the first study reporting the synthesis of monolithic κ-carrageenan aerogels with meso- and macroporous structures, being unique in physical and chemical properties. We demonstrate a novel method to synthesize κ-carrageenan aerogels in which potassium thiocyanate was used as the source of specific ions. Aerogels were characterized by envelope density analysis, scanning electron microscopy, nitrogen adsorption–desorption analysis, X-ray powder diffractometry and IR spectroscopy. By varying the concentration of κ-carrageenan between 0.5 and 3 wt%, the envelope density can be linearly increased from 40 to 160 kg m−3. The sulphate functional groups in the wet gel and the specific ions are the key factors controlling the volume shrinkage of aerogels which average about 66%. The aerogels exhibit a fibrillar structure similar to cellulose aerogels. The fibril thickness was observed to be 10–15 nm and the specific surface area was about 230 m2 g−1. The existing meso- and macroporous structures were confirmed by nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherm analysis and scanning electron microscopy. The aerogels were completely pure, free of specific ions and confirmed to be amorphous by powder X-ray diffraction. Hence, these porous materials can provide a matrix with a chelating function which can be used as a host in many applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...