Contribution of silica–rubber interactions on the viscoelastic behaviors of modified solution polymerized styrene butadiene rubbers (M-S-SBRs) filled with silica
Abstract
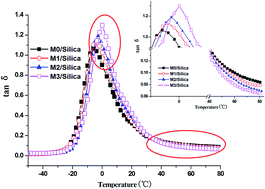
A series of modified solution-polymerized styrene butadiene rubbers (M-S-SBRs) with different molar contents of polar groups were prepared through grafting 3-mercaptopropionic acid into solution-polymerized styrene butadiene rubber (S-SBR) chains. The molar contents of the polar groups in M-S-SBR were calculated using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectroscopy. Thermodynamic analytical methods, including the surface energy of M-S-SBR and filler flocculation, show that the introduction of polar groups increases the work of adhesion of filler–rubber (Wrf), which is an indicator for the compatibility of the filler with rubber. The thermodynamic results can be further proved by TEM micrographs. Strain sweep experiments were carried out to investigate the temperature dependent nonlinear strain-dependence of elastic moduli, referred to as the Payne effect. The filler–filler network and interfacial strength were studied in terms of critical strain γc and activation energy Ea. Dynamic mechanical measurements show that a combination of higher energy dissipation in the low temperature range and higher elasticity in the high temperature region were achieved for M-S-SBR/Silica when compared with their non-modified counterpart.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...