How much do coulombic interactions stabilize a mesophase? Ion pair and non-ionic binary isosteric derivatives of monocarbaborates and carboranes†
Abstract
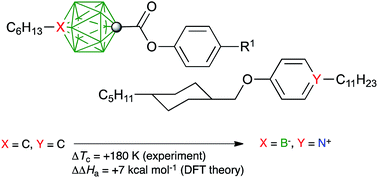
Replacement of the B− atom in the monocarbaborate anion, 1[10] or 1[12], and the N+ atom in the pyridinium cation [Pyr] of a liquid crystalline ion pair with C atoms leads to an isoelectronic and isosteric non-ionic binary liquid crystalline mixture of carborane (2[10] or 2[12]) and benzene ([Ph]) derivatives lacking coulombic interactions. A comparison of mesogenic properties of ion pairs, 1[10]c–[Pyr]c and 1[12]c–[Pyr]c, with their analogous non-ionic mixtures, 2[10]c–[Ph]c and 2[12]c–[Ph]c, shows a 181 K higher clearing temperature, Tc, for the ion pair. This corresponds to a DFT-calculated difference in association energy ΔΔHa = 24.5 kcal mol−1 in a typical dielectric medium (ε = 2.5). Pure compounds and binary mixtures were characterized using thermal, optical, and XRD methods.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...