CdS nanorods assisted thermal oxidation of polythiol segments of PS-b-polythiols to produce core cross-linking micellar clusters†
Abstract
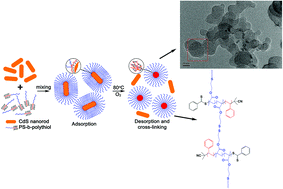
In this paper, we described a new and simple method to produce degradable core cross-linking (CCL) micellar clusters that utilized CdS nanorods to assist thermal oxidation of the polythiol segment of a diblock copolymer, polystyrene-b-polythiol (PS-b-polythiol), at high concentration (2.3 wt%) in a common organic solvent (toluene). The CdS nanorods acted not only as catalysts, but also as templates. The diblock copolymer, PS-b-polythiol, was obtained by aminolysis of polystyrene-b-poly(2-(ethyl-xanthate)ethylmethacrylate) (PS-b-P1), a block copolymer synthesized via reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization using a macroRAFT transfer agent, PS-CTA, and a methacrylate monomer that possessed a protected thiol group, in the presence of n-butylamine and tributyl phosphine. The CdS nanorods were synthesized conveniently by thermolysis of an alkyl xanthate, Cd-HDX. The TEM image clearly showed the formation of micellar clusters and the oxidation procedure was investigated by 1H-NMR and XPS. The formation of core cross-linking (CCL) micelles was confirmed to be reversible by reduction utilizing DTT as the reducing agent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...