New thermal-responsive polymers based on alanine and (meth)acryl amides†
Abstract
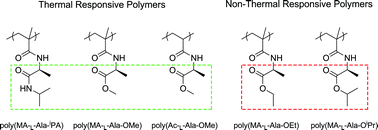
Five (meth)acrylamide derivatives containing alanine ester/amide residues were synthesized and then polymerized using RAFT polymerization. After polymerization and further treatment of the obtained polymers with excess radical initiators, we obtained a series of homopolymers with well-defined molecular weights and end groups. Depending on the structure of side-chain terminal groups, these alanine-containing homopolymers displayed thermal-responsive behaviors in water. Samples containing a methyl ester group, i.e., poly(MA-L-Ala-OMe) and poly(Ac-L-Ala-OMe), showed low critical solution temperature (LCST) behaviors. Replacing methyl ester with ethyl or isopropyl ester groups caused loss of thermal-responsive properties. However, replacing the isopropyl ester with isopropyl amide groups can regain thermal-responsive polymers such as poly(MA-L-Ala-iPA). We further studied the LCST behaviors of these three homopolymers with respect to the degree of polymerization (DP), concentration, salt concentration, and chirality of amino acids. It was found that the cloud point (CP) decreased with increasing polymer concentration, DP and salt concentration. The CPs of the polymers prepared from a pair of enantiomers showed no distinct difference, while the random copolymer of the two enantiomers displayed higher CP than optically pure homopolymers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...