Biocompatible and thermo-responsive nanocapsule synthesis through vesicle templating†
Abstract
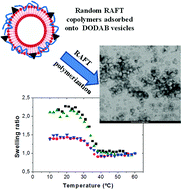
Thermo-responsive and biocompatible cross-linked nanocapsules were synthesized through dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide (DODAB) vesicle templating. For this, firstly two random copolymers, N-vinylcaprolactam (VCL) and acrylic acid (AA), with different chain lengths but using the same monomer ratio, were synthesized by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. These anionic random copolymers were adsorbed onto cationic DODAB vesicles. Then, biocompatible and thermo-responsive nanocapsules were obtained by semicontinuous emulsion polymerization under monomer-starved conditions for both the main monomer (VCL) and the cross-linker. Although in all the cases the typical thermal behavior of PVCL-based nanocapsules was observed, hysteresis between cooling and heating cycles was observed at low temperature in the case of non-cross-linked nanocapsules. This behavior was reduced using different types and amounts of cross-linkers. In addition, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) characterization demonstrated the successful formation of nanocapsules either with short or long random copolymers. The formation of stable nanocapsules was confirmed below and above the volume phase transition temperature (VPTT) by surfactant lysis experiments through optical density and DLS measurements in all the nanocapsules synthesized. These biocompatible and thermo-responsive nanocapsules could be suitable and potentially useful as nanocarriers for drug delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...