Sunlight-promoted photocatalytic hydrogen gas evolution from water-suspended cellulose: a systematic study†
Abstract
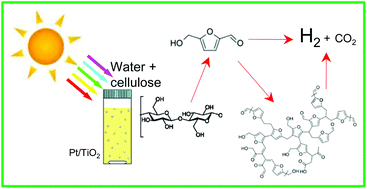
This work presents a systematic study of cellulose (CLS) as a sacrificial biomass for photocatalytic H2 evolution from water. The idea is indeed to couple a largely available and not expensive biomass, and water, with a renewable energy like solar radiation. An aqueous CLS suspension irradiated either at 366 nm (UV-A) or under sunlight in the presence of Pt/TiO2 behaves as a H2 evolving system. The effects of irradiation time, catalyst and CLS concentrations, pH and water salinity are studied. Addition of CLS to the sample significantly improved H2 evolution from water splitting, with yields up to ten fold higher than those observed in neat water. The mechanism of the photocatalytic process relies on the TiO2-mediated CLS hydrolysis, under irradiation. The polysaccharide depolymerisation generates water-soluble species and intermediates, among them 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) was identified. These intermediates are readily oxidized following the glucose photoreforming, thus enhancing water hydrogen ion reduction to give gas-phase H2. The formation of “colored” by-products from HMF self-polymerization involves a sort of “in situ dye sensitization” that allows an effective photoreaction even under solar light. The procedure is evaluated and successfully extended on cellulosic biomasses, i.e. rice husk and alfalfa (Medicago sativa) stems, not previously investigated for this application.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...