Photodynamic decontamination of foodstuff from Staphylococcus aureus based on novel formulations of curcumin
Abstract
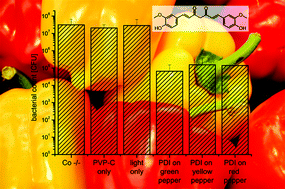
Increasing antibiotic resistance is one of the world's greatest health problems. The food chain is an important factor in the transfer of resistant germs from animals to humans. This study focuses on photodynamic inactivation (PDI), employing curcumin bound to polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP-C) and NovaSol®-curcumin as photosensitizers, as potent tool for the decontamination of cucumber, pepper and chicken meat from Staphylococcus aureus (serving as the model for methicillin-resistant S. aureus, MRSA). Both curcumin and PVP have been approved as food additives, consequently exhibiting excellent biocompatibility. Vegetables and meat were contaminated with S. aureus and sprinkled with PVP-C and NovaSol®-curcumin at concentrations of 50 and 100 μM, respectively. Illumination was performed immediately using visible light (435 nm, 9.4 mW cm−2, 33.8 J cm−2). The PDI efficiency was determined by quantitative analyses of colony forming units 24 h post illumination. Additionally, the long-term effects of the photodynamic inactivation on cucumbers were investigated by quantitative analyses of the viable bacterial fraction after 24 and 48 h. Photodynamic inactivation of S. aureus revealed a mean reduction of 2.6 log10 (99.8%) for cucumbers, 2.5 log10 (99.7%) for pepper and 1.7 log10 (98%) for chicken meat relative to control samples. The bactericidal effect compared to controls seems to last for at least 48 h. Furthermore, no visible changes of the exterior appearance of foodstuff after photodynamic decontamination were observed. Photodynamic inactivation may therefore constitute a safe, economic and effective decontamination technique, which is harmless to health and not noticeable to consumers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...