Monitoring plasmon-driven surface catalyzed reactions in situ using time-dependent surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on single particles of hierarchical peony-like silver microflowers†
Abstract
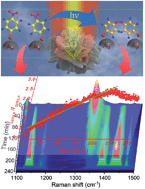
Investigating the kinetics of catalytic reactions with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) on a single particle remains a significant challenge. In this study, the single particle of the constructed hierarchical peony-like silver microflowers (SMFs) with highly roughened surface led to the coupling of high catalytic activity with a strong SERS effect, which acts as an excellent bifunctional platform for in situ monitoring of surface catalytic reactions. The kinetics of the reaction of 4-nitrothiophenol (4-NTP) dimerizing into 4,4′-dimercaptoazobenzene (DMAB) was investigated and comparatively studied by using the SERS technique on a single particle of different morphologies of SMFs. The results indicate that a fully developed nanostructure of a hierarchical SMF has both larger SERS enhancement and apparent reaction rate constant k, which may be useful for monitoring and understanding the mechanism of plasmon-driven surface catalyzed reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...