Quantum dot-functionalized porous ZnO nanosheets as a visible light induced photoelectrochemical platform for DNA detection
Abstract
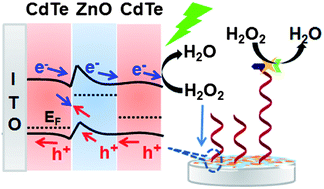
This work reports the synthesis of novel CdTe quantum dot (QD)-functionalized porous ZnO nanosheets via a covalent binding method with (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane as a linker. The functional nanosheets showed an excellent visible-light absorbency and much higher photoelectrochemical activity than both CdTe QDs and ZnO nanosheets due to the porous structure and appropriate band alignment between the CdTe QDs and ZnO nanosheets. Using hydrogen peroxide as an electron acceptor the nanosheet-modified electrode showed a sensitive photocurrent response. This speciality led to a novel methodology for the design of hydrogen peroxide-related biosensors by the formation or consumption of hydrogen peroxide. Using biotin-labeled DNA as capture probe, a model biosensor was proposed by immobilizing the probe on a nanosheet-modified electrode to recognize target DNA in the presence of an assistant DNA, which produced a “Y” junction structure to trigger a restriction endonuclease-aided target recycling. The target recycling resulted in the release of biotin labeled to the immobilized DNA from the nanosheet-modified electrode, thus decreased the consumption of hydrogen peroxide by horseradish peroxidase-mediated electrochemical reduction after binding the left biotin with horseradish peroxidase-labeled streptavidin, which produced an increasing photoelectrochemical response. The ‘signal on’ strategy for photoelectrochemical detection of DNA showed a low detection limit down to the subfemtomole level and good specificity to single-base mismatched oligonucleotides. The sensitized porous ZnO nanosheets are promising for applications in both photovoltaic devices and photoelectrochemical biosensing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...