A positron annihilation spectroscopic investigation of europium-doped cerium oxide nanoparticles†
Abstract
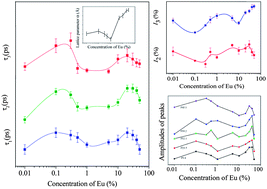
Doping in ceria (CeO2) nanoparticles with europium (Eu) of varying concentrations (0, 0.1, 0.5, …, 50 atom%) is studied using complementary experimental techniques and novel observations were made during the investigation. The immediate observable effect was a distinct reduction in particle sizes with increasing Eu concentration attributed to the relaxation of strain introduced due to the replacement of Ce4+ ions by Eu3+ ions of larger radius. However, this general trend was reversed in the doping concentration range of 0.1–1 atom% due to the reduction of Ce4+ to Ce3+ and the formation of anion vacancies. Quantum confinement effects became evident with the increase of band gap energy when the particle sizes reduced below 7–8 nm. Positron annihilation studies indicated the presence of vacancy type defects in the form of vacancy clusters within the nanoparticles. Some positron annihilation was also seen on the surface of crystallites as a result of diffusion of thermalized positrons before annihilation. Coincidence Doppler broadening measurements indicated the annihilation of positrons with electrons of different species of atoms and the characteristic S–W plot showed a kink-like feature at the particle sizes where quantum confinement effects began.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...