The visible light-driven photocatalytic degradation of Alizarin red S using Bi-doped TiO2 nanoparticles
Abstract
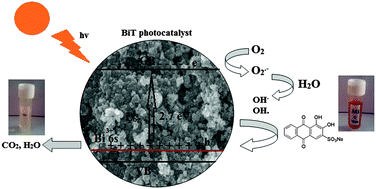
In this paper we report the preparation of a series of Bi3+-doped TiO2 nanoparticles with different Bi-concentrations, i.e. 0.25–5% by a facile sol–gel process and their application as an efficient photocatalyst. The detailed characterization revealed that the Bi-doped TiO2 catalysts possess densely grown nanoparticles, a high specific surface area, crystalline anatase TiO2 and good optical properties. The incorporation of Bi3+ into the TiO2 lattice led to the expansion of the TiO2 spectral response into the visible light region and the efficient separation of charge carriers. The prepared samples were employed for the photocatalytic degradation of Alizarin red S dye (ARS) under visible light illumination. It was found that the incorporation of the Bi3+ ions in the TiO2 lattice causes a marked improvement in the photocatalytic degradation of the ARS dye; however, the degradation efficiency depended upon the Bi+3 ion doping concentration and the dose of the prepared catalyst. The detailed photocatalytic experiments confirmed that the 1% Bi+3 ion doping concentration and 0.1 g L−1 dose exhibited the best photocatalytic degradation efficiencies for the model dye. Moreover, more than 80% degradation of ARS was observed by the prepared Bi-doped catalysts within 90 minutes under visible light. The synthesized Bi-doped TiO2 nanoparticles revealed a superior photocatalytic behavior towards the photocatalytic degradation of ARS under similar experimental conditions, as compared to the synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles and other commercially available derivatives (TiO2 PC-50 and TiO2 P25).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...