A CoMSIA study to design antagonist ligands for the LuxS protein
Abstract
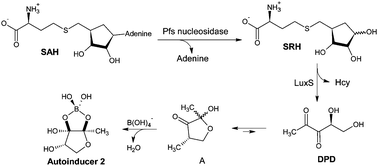
LuxS is an important protein involved in the synthesis of Autoinducer 2, the signaling molecule in the quorum sensing system for the communication of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Therefore, the LuxS protein is a potential target for inhibiting the production of biological phenomena in pathogenic bacteria that could control several diseases such as periodontal disease and caries among others. A comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA) study was conducted with 20 analogues of ribosylhomocysteine (RHC) and KRI, which are native ligands of the LuxS protein. Due to the change of the oxygen atom in position 7 in the proposed inhibitor INH-KRI 02 for the sulfur atom and the stereochemistry of the carbon in position 4, there was a possible variation of the hydrophobic, hydrogen bond donor and acceptor fields, which were observed as predominant over the steric and electrostatic fields in the obtained dockings. The presence of a sulfur atom can be fundamental in the inhibition of the LuxS protein. This increase seems to improve the lipophilicity due to changes of atoms in several positions, indicating an improvement in the predicted activity of the ligands compared with other previously described ligands.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...