Benzothiazolyl substituted iminothiazolidinones and benzamido-oxothiazolidines as potent and partly selective aldose reductase inhibitors†
Abstract
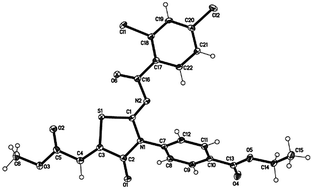
Two new series of oxothiazolidine benzoate and acetate derivatives were synthesized and evaluated as aldehyde reductase (ALR1) and aldose reductase (ALR2) inhibitors. Methyl 2-[2-benzamido-3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-4-oxothiazolidin-5-ylidene]acetates (2a–k) and ethyl 4-[2-benzamido-5-(2-methoxy-2-oxyethylidene)-4-oxothiazolidin-3-yl]benzoates (4a–j) were obtained in good to excellent yield by the heterocyclization of 1-aroyl-3-(2-benzothiazolyl) thioureas (1a–j) and ethyl 4-(3-aroylthioureido)benzoates (3a–j), respectively, with dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate (DMAD) in dry methanol. Among the tested compounds, 2d, 2g, 2h, 2i, 2j, 4b, 4f and 4h showed a potent inhibitory activity on ALR1, whereas 2a, 2g, 2h, 4d, 4f, 4h and 4j exhibited potent inhibition on ALR2. Docking analysis suggested the likely binding modes of the inhibitors within the active site of ALR2. The new aldose reductase inhibitors are believed to represent useful lead structures for the generation of candidate compounds to target a number of pathological conditions, most notably long-term diabetic complications. FTIR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, GC-MS and elemental analyses confirmed the assigned structures to the synthesized compounds. Further, the structure and geometry of compound ethyl 4-((2Z,5Z)-22,4-di-(2,4-dichlorobenzoylimino)-5-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethylidene)-4-oxothiazolidin-3-yl)benzoate (4c) was unequivocally confirmed by single crystal X-ray diffraction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...