Synthesis and evaluation of a series of quinolinyl trans-cyanostilbene analogs as anticancer agents
Abstract
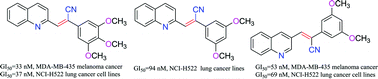
A series of novel trans-2-quinolyl-, 3-quinolyl- and 4-quinolyl cyanostilbene derivatives were synthesized as analogs of combretastatin A-4 (CA-4), and evaluated for anticancer activity against a panel of 60 human cancer cell lines. The quinolin-2-yl and quinolin-3-yl analogs containing trimethoxyphenyl (10 and 16, respectively) or dimethoxyphenyl (12 and 18, respectively) moieties showed growth inhibition against all the cancer cell lines in the panel, with GI50 values generally <1 μM. Quinolin-2-yl-analog 10 exhibited potent growth inhibition against MDA-MB-435 melanoma and NCI-H522 non-small cell lung cancer line with GI50 values of 33 nM and 37 nM respectively. Quinolin-2-yl-analog 12 showed potent growth inhibition against NCI-H522 non-small cell lung cancer lines with a GI50 value of 94 nM. Quinolin-3-yl-analog 18 exhibited potent growth inhibition against MDA-MB-435 melanoma and NCI-H522 non-small cell lung cancer lines with GI50 values of 53 nM and 69 nM, respectively. Thus, structural modification of the CA-4 molecule has afforded compounds with potential clinical utility in the treatment a variety of different solid tumors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...