Synthesis and evaluation of artesunate–indoloquinoline hybrids as antimalarial drug candidates†
Abstract
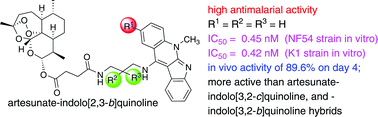
Hybrids of artesunate–indolo[2,3-b]quinoline, –indolo[3,2-c]quinoline, and –indolo[3,2-b]quinoline were synthesized and screened for their antiplasmodial activity against two different malaria strains (CQS and CQR) and their cytotoxic activities against normal cells were evaluated. All the synthesized hybrids showed a decreased cytotoxicity and increased antimalarial activity relative to the individual, non-hybridized compounds. Furthermore, these hybrids were stronger β-haematin inhibitors than the corresponding molecules from which they were derived. The most effective antimalarial hybrid showed an IC50 value of 0.45 nM against the CQS strain. At the same time this hybrid also showed effective activity against the CQR strain, with an IC50 value of 0.42 nM and an RI value of 0.93. With the dosing of the artesunate–indolo[2,3-b]quinoline set at 10 mg kg−1 once a day for four consecutive days, parasitemia was significantly reduced on day 4, with an antiparasitic activity of 89.6%, and a mean mouse survival time of 7.7 days.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...