Identifying the potential extracellular electron transfer pathways from a c-type cytochrome network
Abstract
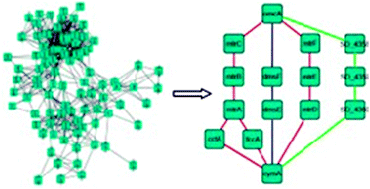
Extracellular electron transfer (EET) is the key feature of some bacteria, such as Geobacter sulfurreducens and Shewanella oneidensis. Via EET processes, these bacteria can grow on electrode surfaces and make current output of microbial fuel cells. c-Type cytochromes can be used as carriers to transfer electrons, which play an important role in EET processes. Typically, from the inner (cytoplasmic) membrane through the periplasm to the outer membrane, they could form EET pathways. Recent studies suggest that a group of c-type cytochromes could form a network which extended the well-known EET pathways. We obtained the protein interaction information for all 41 c-type cytochromes in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, constructed a large-scale protein interaction network, and studied its structural characteristics and functional significance. Centrality analysis has identified the top 10 key proteins of the network, and 7 of them are associated with electricity production in the bacteria, which suggests that the ability of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 to produce electricity might be derived from the unique structure of the c-type cytochrome network. By modularity analysis, we obtained 5 modules from the network. The subcellular localization study has shown that the proteins in these modules all have diversiform cellular compartments, which reflects their potential to form EET pathways. In particular, combination of protein subcellular localization and operon analysis, the well-known and new candidate EET pathways are obtained from the Mtr-like module, indicating that potential EET pathways could be obtained from such a c-type cytochrome network.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...