Structural and functional investigation of zebrafish (Danio rerio) NOD1 leucine rich repeat domain and its interaction with iE-DAP†
Abstract
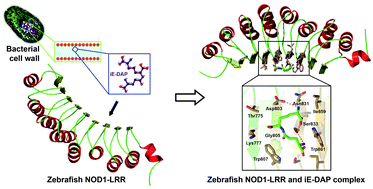
Nucleotide binding and oligomerization domain 1 (NOD1), a cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor (PRR) and is a key component for modulating innate immunity and signaling. It is highly specific to γ-D-Glu-mDAP (iE-DAP), a cell wall component of Gram-negative and few Gram-positive bacteria. In the absence of the experimental structure of NOD1 leucine rich repeat (NOD1-LRR) domain, the NOD signaling cascade mediated through NOD1 and iE-DAP interaction is poorly understood. Herein, we modeled 3D structure of zebrafish NOD1-LRR (zNOD1-LRR) through a protein-threading approach and structural integrity of the model was assessed using molecular dynamics simulations. Molecular interaction analysis of iE-DAP and zNOD1-LRR, their complex stability and binding free energy studies were conducted to anticipate the ligand binding residues in zNOD1. Our study revealed that His775, Lys777, Asp803, Gly805, Trp807, Asn831, Ser833, Ile859 and Trp861 situated in the β-sheet region of zNOD1-LRR could be involved in iE-DAP recognition, which correlates the earlier findings in human. Comparison of binding free energies of native and mutant zNOD1–iE-DAP complexes delineated His775, Lys777, Asp803, Ser833 and Ile859 as the pivotal residues for energetic stability of NOD1 and iE-DAP interaction. This study provides the first comprehensive description of biophysical and biochemical parameters responsible for NOD1 and iE-DAP interaction in zebrafish, which is expected to shed more light on NOD1 signaling and therapeutic applications in other organisms.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...