Vitamin C exerts beneficial hepatoprotection against Concanavalin A-induced immunological hepatic injury in mice through inhibition of NF-κB signal pathway
Abstract
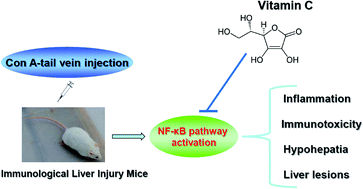
The present study was designed to investigate the potential benefits of vitamin C (VC) in treating immunological liver injury induced by Concanavalin A (Con A, 20 mg kg−1) in mice. Interestingly, VC administration significantly reduced serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and total-bilirubin (T-bilirubin) in Con A-lesioned mice, while serum concentrations of albumin and total-protein (T-protein) were increased. Moreover, inflammatory cytokine profiles, such as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-8 (IL-8), were decreased in liver tissue by VC administration. Morphological examination showed that Con A-induced liver damage was effectively mitigated. As shown in RT-PCR assay, VC administration resulted in down-regulated mRNA expressions of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). In addition, VC contributed towards the reduction of intrahepatic tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and the receptor (TNF-R) protein levels, as well as decreasing IKKβ, p-IκBα, p50 and NF-κB expressions; furthermore, VC blocked intranuclear DNA-binding NF-κB locus. Our findings show that VC effectively attenuates Con A-mediated immunotoxicity in liver tissue, through an underlying mechanism which relates to dampening of the intrahepatic NF-κB signal pathway, thereby reducing cytotoxicity within hepatocytes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...