Optical excitation of MgO nanoparticles; a computational perspective†
Abstract
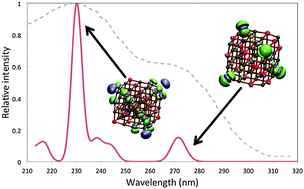
The optical absorption spectra of magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles, along with the atomic centres responsible, are studied using a combination of time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) and coupled-cluster methods. We demonstrate that TD-DFT calculations on MgO nanoparticles require the use of range-separated exchange–correlation (XC-) functionals or hybrid XC-functionals with a high percentage of Hartree–Fock like exchange to circumvent problems related to the description of charge-transfer excitations. Furthermore, we show that the vertical excitations responsible for the experimentally studied range of the spectra of the MgO nanoparticles typically involve both 3-coordinated corner sites and 4-coordinated edge sites. We argue therefore that to label peaks in these absorption spectra exclusively as either corner or edge features does not provide insight into the full physical picture.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...