Highly monodisperse multiple twinned AuCu–Pt trimetallic nanoparticles with high index surfaces†
Abstract
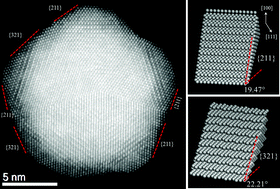
Trimetallic nanoparticles possess different properties than their mono- and bi-metallic counterparts, opening a wide range of possibilities for diverse potential applications with the notion to study possible morphology, atomic ordering, reduce precious metal consumption and many others. In this paper, we present a comprehensive experimental study on AuCu–Pt trimetallic nanoparticles with an average diameter of 15 ± 1.0 nm, synthesized in a one-pot synthesis method and characterized by the Cs-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy technique that allowed us to probe the structure at the atomic level resolution. A new way to control the nanoparticle morphology by the presence of third metal (Pt) is also discussed by the overgrowth of Pt on the as prepared AuCu core by Frank–van der Merwe (FM) layer-by-layer and Stranski–Krastanov (SK) island-on-wetting-layer growth modes. With the application of this research, we are now a step closer to produce optimum catalysts in which the active phase forms only surface monolayers. In addition, the nanoalloy exhibits high index facet surfaces with {211} and {321} families that are highly open-structure surfaces and are interesting for the catalytic applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...