Dissecting the steps of CO2 reduction: 1. The interaction of CO and CO2 with γ-Al2O3: an in situ FTIR study†
Abstract
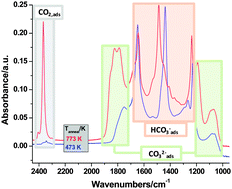
The adsorption of CO2 and CO was investigated on a pure γ-Al2O3 support material that has been used in Pd and Ru catalysts for the reduction of CO2. The adsorption of CO2 resulted in the formation of carbonates, bicarbonates and linearly adsorbed CO2 species. The amount and the nature of the adsorbed species were dependent on the annealing temperature of the alumina support. On γ-Al2O3 annealed at 473 K mostly bicarbonates formed, while no adsorbed CO2 was seen on this highly hydroxylated surface. With increasing calcination temperature the amount of both surface carbonates and linearly adsorbed CO2 increased, but still the most abundant surface species were bicarbonates. Surface carbonates and adsorbed CO2 can readily be removed from the alumina surface, while bicarbonates are stable to elevated temperatures. The interaction of CO with γ-Al2O3 is much weaker than that of CO2. At room temperature CO adsorbs only on Lewis acid sites, and can be readily removed by evacuation. At 100 K CO can probe different defect sites on the alumina surface. Under no conditions we have observed the formation of any carbonates or bicarbonates upon the interaction of CO with the pure alumina support. In co-adsorption experiments CO competes for adsorption sites with the linearly adsorbed CO2 on the 773 K-annealed γ-Al2O3 surface, but it does not result in the desorption of CO2, rather in the increased production of weakly held carbonates. After the removal of adsorbed CO, CO2 moves back to its original adsorption sites, i.e., Lewis acidic Al3+ centers. The exposure of a CO2-saturated γ-Al2O3 to H2O did not affect any of the adsorbed surface species. The findings of this study will be used to rationalize the results of our ongoing in situ and in operando studies on the reduction of CO2 on supported Pd and Ru catalysts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...