Structure–properties relationship of carbazole and fluorene hybrid trimers: experimental and theoretical approaches†
Abstract
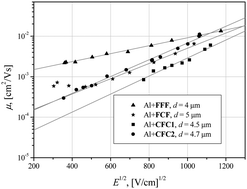
Synthesis and properties of fluorene and carbazole derivatives having three electrophores per molecule with different architectures are reported. The synthesized compounds possess high thermal stabilities with 5% weight loss temperatures exceeding 350 °C. They form glasses with glass transition temperatures ranging from 60 to 68 °C. Cyclovoltammetric experiments revealed the high electrochemical stability of the fluorene trimer. In contrast, 2- and 2,7-fluorenyl substituted carbazole derivatives show irreversible oxidation in the CV experiments. The electron photoemission spectra of the films of the synthesized compounds revealed ionization potentials of 5.65–5.89 eV. Hole drift mobilities in the amorphous layers of the synthesized compounds reach 10−2 cm2 V−1 s−1 at high electric fields, as established by a xerographic time-of-flight technique. DFT calculations show that HOMO and LUMO orbitals of the compounds are very similar in energy and shape. The similar hole mobilities observed for the three compounds are discussed in the frame of the Marcus theory. An important influence of the alkyl groups on the ionization potentials and on the hole mobilities was also observed and its origin is discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...