Synthesis of cholic acid-core poly(ε-caprolactone-ran-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol) 1000 random copolymer as a chemotherapeutic nanocarrier for liver cancer treatment
Abstract
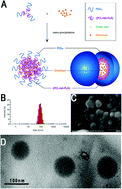
A star-shaped random copolymer, cholic acid functionalized poly(ε-caprolactone-ran-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol) 1000 (CA-(PCL-ran-PLA)-b-PEG1k), was synthesized by a core-first approach involving three stages of chemical reactions, and was characterized by hydrogen-1 nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR), gel permeation chromatography and thermogravimetric analysis. The docetaxel-loaded nanoparticles (NPs) were prepared by a modified nano-precipitation method. The formation and characterization of these NPs were confirmed through dynamic light scattering, zeta potential measurements, field emission scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The in vitro release profiles indicated that CA-(PCL-ran-PLA)-b-PEG1k NPs had excellent sustained and controlled drug release properties. Both confocal laser scanning microscope and flow cytometric results showed that the coumarin-6 loaded CA-(PCL-ran-PLA)-b-PEG1k NPs had the highest cellular uptake efficiency compared with PEG1k-b-(PCL-ran-PLA) NPs and CA-(PCL-ran-PLA) NPs in human hepatic carcinoma cells. The docetaxel-loaded CA-(PCL-ran-PLA)-b-PEG1k NPs were also proved to have the highest drug loading content, encapsulation efficiency, and the best anti-tumor efficacy both in vitro and in vivo. In conclusion, the star-shaped CA-(PCL-ran-PLA)-b-PEG1k copolymer was successfully synthesized and could be used as a promising drug-loaded biomaterial for liver cancer chemotherapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...