Applicability of the bismuth bulk rotating disk electrode for heavy metal monitoring in undisturbed environmental and biological samples: determination of Zn(ii) in rainwater, tap water and urine
Abstract
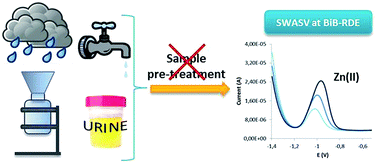
The bismuth bulk rotating disk electrode (BiB-RDE) is investigated here as a new and advantageous alternative to determine heavy metal ions in undisturbed environmental and biological samples (pH 7.5) by anodic stripping voltammetry, with demonstrated applicability to the determination of Zn(II) in rainwater, tap water and urine. The proposed method benefits from the insensitiveness of the bismuth bulk electrode to the Bi(III) hydrolysis that affects the common “in situ” Bi film approach preventing its use at intermediate to alkaline pH. Instrumental parameters such as the rotation speed, deposition time, frequency, amplitude and step potential were optimized for Zn(II) and Cd(II) stripping signal enhancement. The stripping response is linear in the 20–160 μg L−1 concentration range (for 120 s deposition) with detection limits of 8.09 and 11.5 μg L−1 for Zn(II) and Cd(II), respectively. The accuracy of the results obtained was assessed successfully for Zn(II) determination by voltammetric measurements of surface water and wastewater certified reference materials. Applicability to Zn(II) determination in rainwater, tap water and urine was demonstrated by a good correlation with ICP-MS. Our results open a new application field for stripping voltammetry at bismuth electrodes, for heavy metal determination and speciation in environmental and biological samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...