Polypyrrole derivatives as solvent vapor sensors
Abstract
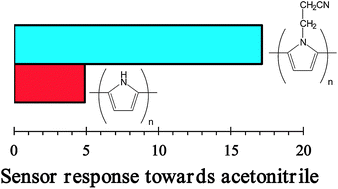
Quantum mechanical calculations have been carried out to investigate the affinity of polypyrrole (PPy) and poly[N-(2-cyanoethyl)pyrrole] (PNCEPy) towards molecules from vapors of different solvents (i.e. water, methanol, acetonitrile and chloroform). Results show that neutral cyano-containing polymers interact more favorably with both water and methanol than neutral PPy, whereas these affinities are the opposite for materials in the oxidized state. Moreover, addition of the geometric distortion contributions and the thermodynamic corrections to the interaction energies allow us to conclude that the binding affinities between the two neutral polymers and small polar molecules in the vapor phase are similar, in excellent agreement with experimental information. On the other hand, the affinity of the two conducting polymers towards chloroform is relatively poor independently of the oxidation state, while acetonitrile interacts more favorably with the N–H of PPy than with the cyano group. The influence of both the vapor molecules and the solvent on the geometric parameters (i.e. dihedral angles, inter-ring bond lengths and bond length alternation pattern) and electronic properties (i.e. ionization potential and π–π* lowest transition energy) have been evaluated using different approaches, which include time-dependent density functional theory calculations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...