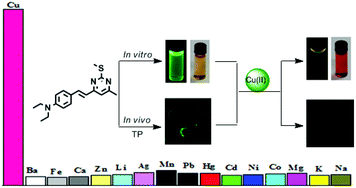
Biological metal detecting, small molecule probes bearing nonlinear optical (NLO) response provide powerful alternatives due to their favorable photophysical properties (e.g. excitation wavelength in the near-IR region), cell permeability (due to their size), and chemical structure flexibility. Here, we present a series of pyrimidine-based NLO biological metal probes, especially a novel copper specific one which taken into account of the small volume-scaled and low cost-scaled nonlinear optical response of TPP and TPP–Cu2+ discussed in our present work. The photophysical properties of the probes were thoroughly investigated. 1H NMR and theoretical computation prove the binding interaction between the probe and the copper ion, which supports the functions of the molecule as a fluorescence signaling unit showing strong fluorescence quenching upon copper metal ion binding. On the other hand, the two-photon absorption cross-section of the novel copper probe increased from 275 to 591 GM (λex = 830 nm) after interacting with copper ion. It was further demonstrated that the NLO response for the copper(II) ion probe could be used for biological copper detection in live cells.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...