Cationic cyanine dyes: impact of symmetry-breaking on optical absorption and third-order polarizabilities†
Abstract
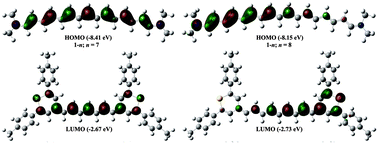
A systematic study is carried out to find the exact crossover point from symmetric to asymmetric configurations (symmetry-breaking) in a series of cationic cyanine dyes. Hybrid density functional with varying exact-exchange admixture has been used to understand the impact of HF exchange both in the gas phase and in the presence of dielectric medium. This approach provides a basis for understanding the electronic structure and photophysical properties of cyanine dyes. The crossover points predicted using this method are in good agreement with the experiment. The SAC-CI method is used to evaluate the lowest S0 → S1 transition energies in the gas phase. These transitions are preferably dominated by the promotion of an electron from HOMO → LUMO. The average static third-order polarizabilities, 〈γ〉, are obtained within the three-state model approximation. The analysis showed that for symmetric cyanines, the calculated 〈γ〉 values are large and negative, mainly originated from the large S0 → S1 transition moments and small S0 → S1 transition energies. For asymmetric cyanines, the 〈γ〉 values are positive and mainly originate from the large change in the ground and first excited state dipole moments. However, both configurations do not include contributions from the two-photon absorption. Further, the localization of charge densities in the HOMO and LUMO indicates that the symmetric and asymmetric cyanines act as promising materials for molecular wires and molecular switches which are fundamental building blocks for molecular electronic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...