Analysis of rosuvastatin stress degradation behavior using liquid chromatography coupled to ultraviolet detection and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry†
Abstract
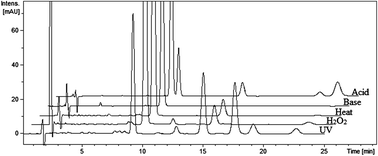
A validated sensitive stability-indicating LC-UV-ESI-MS method was established to analyze rosuvastatin calcium (ROS) and its potential degradation products (DPs). ROS was subjected to different stress conditions recommended by ICH guidelines including photolytic, oxidative, thermal, acidic and basic hydrolysis. Successful separation of the drug from its DPs was achieved on a Zorbax Eclipse Plus C18 column (4.6 × 100 mm, 3.5 μm) using acetonitrile : 0.1% formic acid in water (40 : 60, v/v) as the mobile phase. The flow rate was 0.5 mL min−1 and the sample was detected simultaneously using a UV detector at 242 nm and an ESI-MS detector. ROS was found to be sensitive to photolysis and acidic hydrolysis and slightly affected by oxidation and heat. The proposed chemical structures of the DPs were characterized by studying their fragmentation patterns using ion trap-MS. DPs having different molecular masses including 481, 497, 479, 463 and 513 were produced under different stress conditions. A major DP released upon oxidation was proposed to be rosuvastatin-N-oxide. The ESI-MS response factors of potential DPs were concluded by a simple statistical procedure. Validation parameters including linearity, accuracy, precision, robustness, and specificity were evaluated. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were 15 and 50 pg μL−1 for MS detection and were 1 and 2.5 ng μL−1 for UV detection, respectively. The relative standard deviation values of intraday and interday precision were not more than 1.92% and 1.81%, respectively. The proposed method was successfully applied on ROS tablets concerning drug assay and purity testing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...